Data has experienced a metamorphosis in its perceived value and management within the corporate sphere. Previously underestimated and frequently discarded, data was often relegated to basic reports or neglected due to a lack of understanding and governance. This limited vision, combined with emerging technologies, led to an overwhelming influx of data, and nowhere for it to go. There was little to no governance or understanding of what data they had, or how long they had it.
In the early 2000s, enterprises primarily used siloed databases, isolated data sets with limited accessibility. The 2010s saw the rise of Data Warehouses, which brought together disparate datasets but often led to bottlenecks. Data Lakes emerged as a solution to store vast quantities of raw data and quickly became swamps without adequate governance. Monolithic IT and data engineering groups would struggle to document, catalog, and secure the growing stockpile of data. Product owners and teams that would want, or need access to data would have to request access and wait. Sometimes those requests would end up in a backlog and forgotten about.
In this new dawn of data awareness, the Data Mesh emerges as a revolutionary concept, enabling organizations to efficiently manage, process, and gain insights from their data. As organizations realize data’s pivotal role in digital transformation, it becomes imperative to shift from legacy architectures to more adaptive solutions, making Data Mesh an attractive option.
The Basics of a Data Mesh
The importance of personalized customer experiences should not be understated. More than ever, consumers are faced with endless options. To stand out from competitors, businesses must use data and customer behavior insights to curate tailored and dynamic customer journeys that both delight and command their audience. Analyze purchasing history, demographics, web activity, and other data to understand your customer, as well as their likes and dislikes. Use these insights to design customized customer experiences that increase conversion, retention, and ultimately, satisfaction.
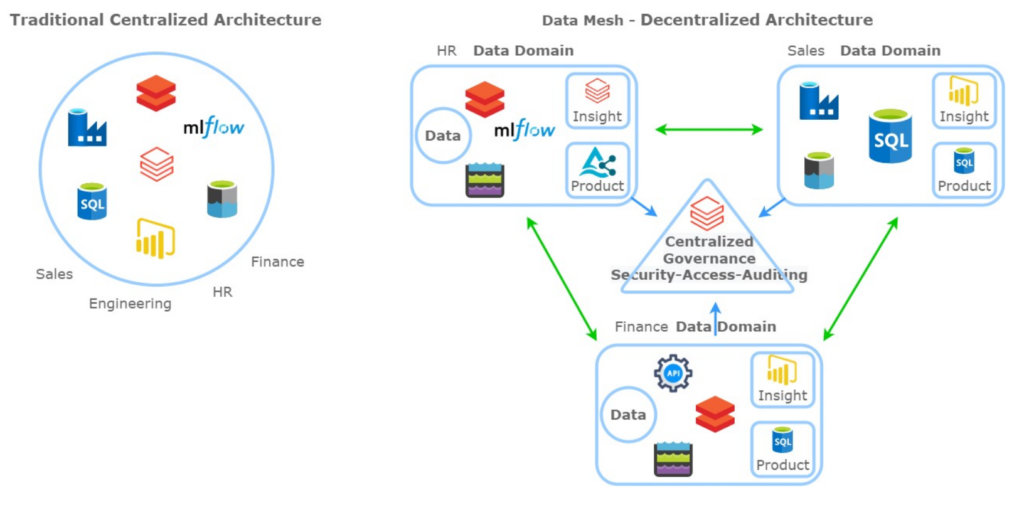
When discussing data architecture concepts, the terms “legacy” or “traditional” imply centralized data management concepts, characterized by monolithic architectures developed and maintained by a data engineering organization within the company. Business units outside of IT would often feel left in the dark, waiting for the data team to address their specific needs and leading to inefficiencies.
First coined in 2019, the Data Mesh paradigm is a decentralized, self-service approach to data architecture. There are four central principles that Data Mesh is based on: Domain ownership, treating data as a product, self-service infrastructure, and federated computational governance.
With Data Mesh, teams (Domains) are empowered to own and manage their data (Product). This requires stewardship at the team level to effectively manage their own resources to ingest, persist and serve data to their end users. Data stewards are responsible for the quality, reliability, security, and accessibility of the data. Data stewards bridge the gap between decentralized teams and enterprise-level governance and oversight.
While teams enjoy autonomy, chaos would ensue without a federated governance approach. This ensures standards, policies and best practices are followed across all product owners and data stewards.
Implementing a Data Mesh requires significant investment in both infrastructure and enhancing teams with the resources and expertise required to manage their own resources. It requires a fundamental change in companies’ mindset of how they treat data.
While a Lakehouse would aim to combine the best of Data Lakes and Data Warehouses, Data Mesh ventures further by decentralizing ownership and control of data. While Data Fabric focuses on seamless data access and integration across disparate sources, Data Mesh emphasizes domain-based ownership. On the other hand, event-driven architectures prioritize real-time data flow and reactions, which can be complementary to Data Mesh.
When and Where to Implement Data Mesh
- Large Organizations with Data Rich Domains: With large organizations, departments often deal with a deluge of data. From Human Resources to Sales, each team has their own requirements for how their data is used, stored, and accessed. As teams consume more data, time to market and development efficiency suffer in centralized architectures. External resources and time constraints are often the biggest issue. By implementing Data Mesh, teams can work independently and take control of their data, increasing efficiency and quality. As a result, teams can optimize and enrich their product offering and cut costs by streamlining ELT/ETL processes and workflows.
With direct control over their data, teams can tune and tailor their data solutions to better meet customer needs.
- Complex Ecosystem: Organizations, especially those operating in dynamic environments with intricate interdependencies, often face challenges in centralized data structures. In such architectures, there’s limited control over resource allocation, utilization, and management, which can hinder teams from maximizing the potential of their data. Centralized approaches can curtail innovation due to rigid schemas, inflexible data pipelines, and lack of domain-specific customization. Data Mesh offers organizations the flexibility to adapt to evolving data needs and utilize domain-specific expertise to curate, process, and consume data tailored to their unique requirements.
- Rapidly growing data environments: Today’s digital age sees organizations collecting data at an unprecedented scale. The sheer volume of data can be overwhelming with the influx of IoT devices, vendor integrations, user interactions, and digital transactions. Centralized teams often grapple with scaling issues, processing delays, and the challenge of timely data delivery. Data Mesh addresses this by distributing the data responsibility across different domains or teams. Multiple decentralized units handle the influx as data inflow increases, ensuring timely processing and reducing system downtime. The result is a more resilient data infrastructure ready to meet both current demands and future needs.
When Not to Implement Data Mesh
- Small to Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs): While Data Mesh presents numerous advantages, it may not be suitable for all organizations or projects. Smaller organizations typically handle lower data volumes and may not possess the resources needed to manage their data independently. In these cases, a centralized data architecture would be more suitable to minimize complications in design and maintenance with fewer resources to manage them.
- Mature and Stable Centralized Architectures: Organizations usually only turn to new solutions when they are experiencing problems. If a well-established centralized architecture is performing and fitting the needs of the company, there isn’t a need necessarily for Data Mesh adoption. Introducing a fundamental change in how data is managed is an expensive and disruptive undertaking. Building new infrastructure and expanding team capabilities changing organizational culture takes time.
- Short-term Projects: Implementing a Data Mesh requires significant time and resource investment. The benefits of a Data Mesh won’t be seen when building or designing a limited lifespan project or proof of concept. If a project’s duration doesn’t justify the investment of a Data Mesh or the scope doesn’t require domain-specific data solutions, then the benefits of a Data Mesh aren’t utilized. Traditional data architectures are usually more appropriate for these applications and don’t need the oversight/governance that a Data Mesh requires.
Opportunities Offered by Data Mesh
- Scalability: Data Mesh enables organizations to scale their data processing capabilities more effectively by enabling teams to control how and when their data is processed, optimizing resource use and costs, and ensuring they remain agile amidst expanding data sources and consumer bases.
- Enhanced Data Ownership: Treating data as a product rather than a byproduct or a secondary asset is revolutionary. By doing so, Data Mesh promotes a culture with a clear sense of ownership and accountability. Domains or teams that “own” their data are more inclined to ensure its quality, accuracy, and relevance. This fosters an environment where data isn’t just accumulated but is curated, refined, and optimized for its intended purpose. Over time, this leads to more prosperous, more valuable data sets that genuinely serve the organization’s needs.
- Speed and Innovation: Decentralization is synonymous with autonomy. When teams have the tools and the mandate to manage their data, they are not bogged down by cross-team dependencies or bureaucratic delays. They can innovate, experiment, and iterate at a faster pace, resulting in expanded data collection and richer data sets. This agility accelerates data product development, enabling organizations to adapt to changing needs quickly, capitalize on new opportunities, and stay ahead of the curve in the competitive market.
- Improved Alignment with Modern Architectures: Decentralization isn’t just a trend in data management; it’s a broader shift seen in modern organizational architectures, especially with the rise of microservices. Data Mesh naturally aligns with these contemporary structures, creating a cohesive environment where data and services coexist harmoniously. This alignment reduces friction, simplifies integrations, and ensures that the entire organizational machinery, services, and data operate in a unified, streamlined manner.
- Enhanced Collaboration: As domains take ownership of their data, there’s an inclination to collaborate with other domains. This cross-functional collaboration fosters knowledge sharing, best practices, and a unified approach to data challenges, driving more holistic insights.
Constraints and Challenges
- Cultural Shift: Teams may not want to own their own data or have the experience to take on the responsibility. Training initiatives, workshops, and even hiring external experts might be necessary to bridge these skill gaps.
- Increased Complexity: Developing an environment that supports a Data Mesh architecture is not without its challenges. As the Data Mesh model expands, managing the growing number of interconnected resources and solving integration issues to ensure smooth communication between various domains can be a considerable obstacle. Planning appropriately to support teams with access, training and management of a Data Mesh is critical to its evolution and success. This includes well defined requirements for APIs, data exchange, and interface protocols.
- Cost Implications: Transitioning to a Data Mesh could entail substantial upfront costs, including hiring additional resources, training personnel, investing in new infrastructure, and possibly overhauling existing systems.
- Governance: Data Governance has become a hot topic as data architectures grow and mature. Ensuring a consistent view of data across all domains can be challenging, especially when multiple teams update or alter their datasets independently. Tools to manage integrity, security and compliance are a requirement in a Data Mesh architecture. The need for teams to have autonomy in a decentralized environment is balanced with a flexible but controlled governance model that is the foundation for federated governance. This can be a challenge when initially designing the model based on team requirements, but it’s an important step to take as early as possible when building a data platform.
Skillset: Evolving with the Data Mesh Paradigm
With an evolved mindset, the Data Mesh paradigm demands expertise that may not have previously been cultivated within traditional data teams. This transition from central data lakes to domain-oriented data products introduces complexities requiring a deep understanding of the data and the specific use cases it serves, both internally and externally. Skills such as collaboration, domain-specific knowledge translation, and data stewardship become vital. As data responsibility becomes decentralized, each team member’s role becomes more critical in ensuring data integrity, relevance, and security. As data solutions evolve, teams must adopt a mindset of perpetual learning, keeping pace with the latest methodologies, tools, and best practices related to managing their data effectively.
Embracing the Data Mesh
In the evolving landscape of data management, the Data Mesh presents a promising alternative to traditional architectures. It’s a journey of empowerment, efficiency, and decentralization. The burgeoning community support for Data Mesh, evident from the increasing number of case studies, forums, and tools developed around it, underscores its pivotal role in the future of data management. However, its success hinges on an organization’s readiness to embrace the cultural and operational shifts it demands. As with all significant transformations, due diligence, meticulous planning, and an understanding of the underlying principles are crucial for its fruitful adoption. Embracing the Data Mesh is more than just a technological shift; it’s a paradigm transformation. Organizations willing to make this leap will find themselves not just keeping up with the rapid pace of data evolution but leading the charge in innovative, data-driven solutions.